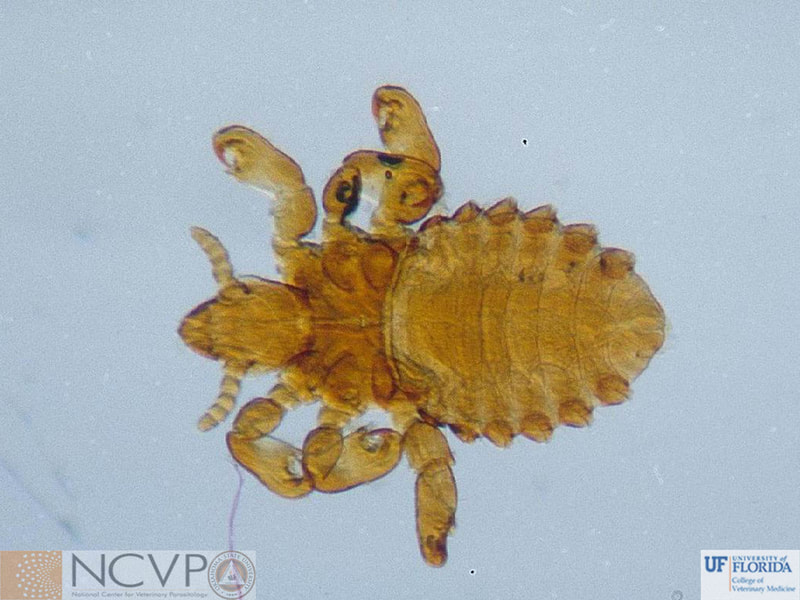
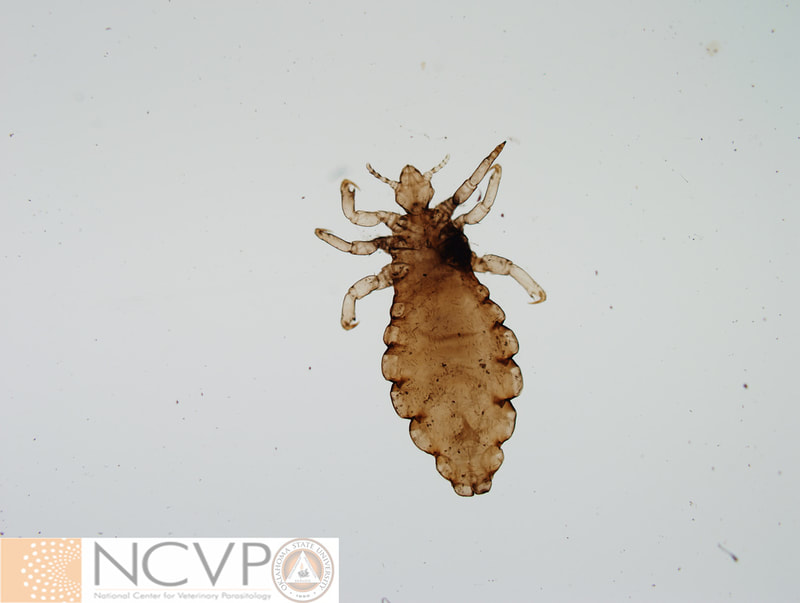
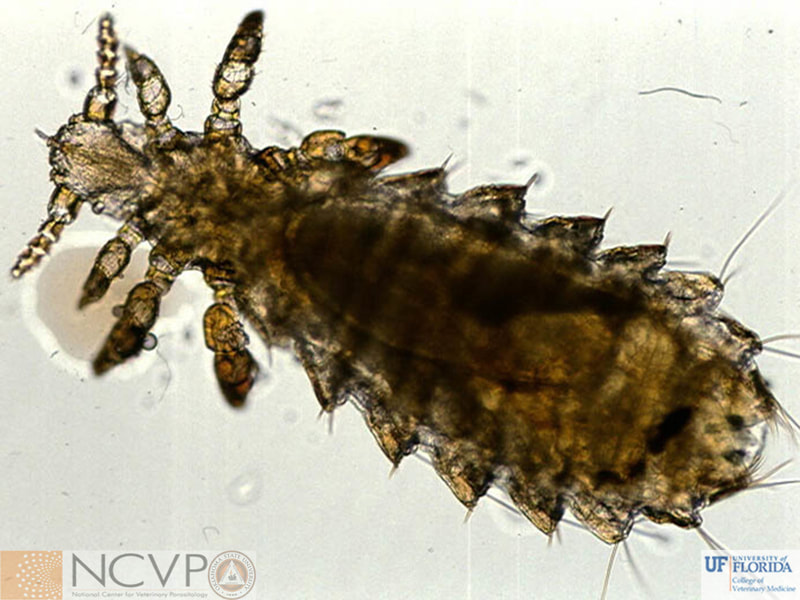
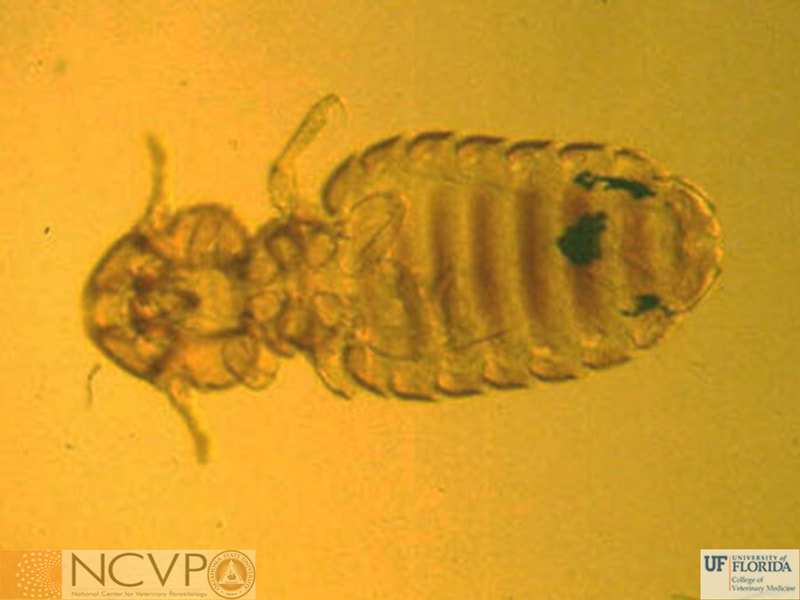
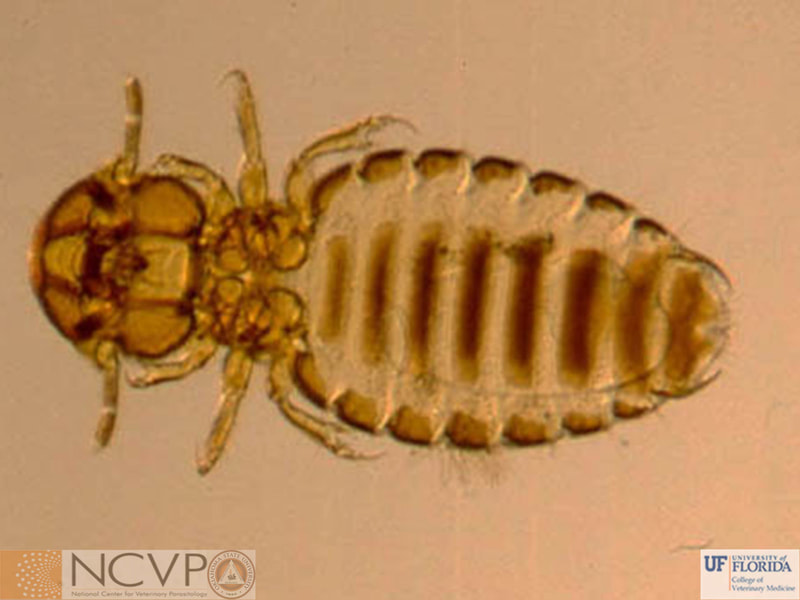
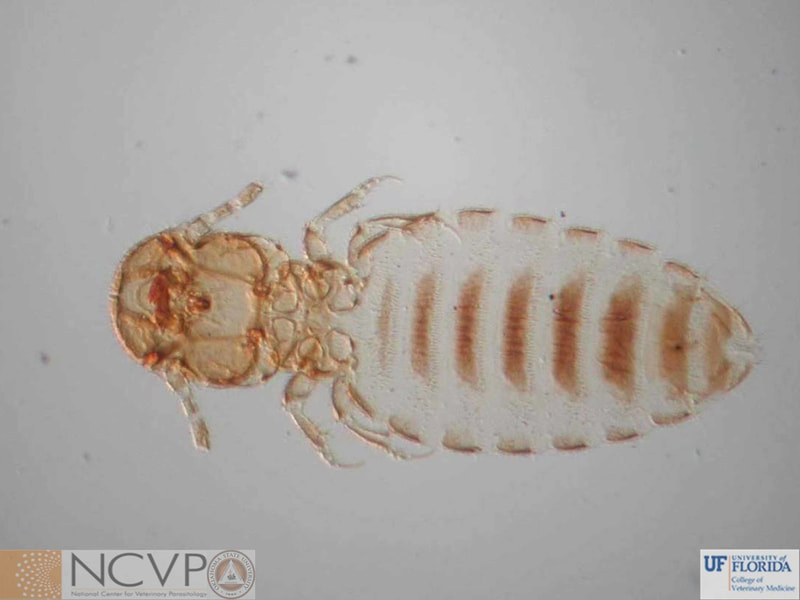
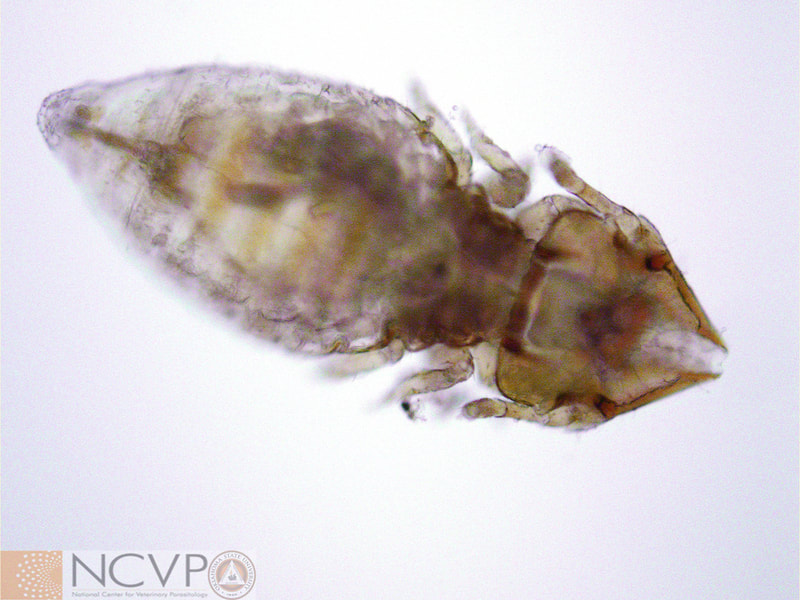
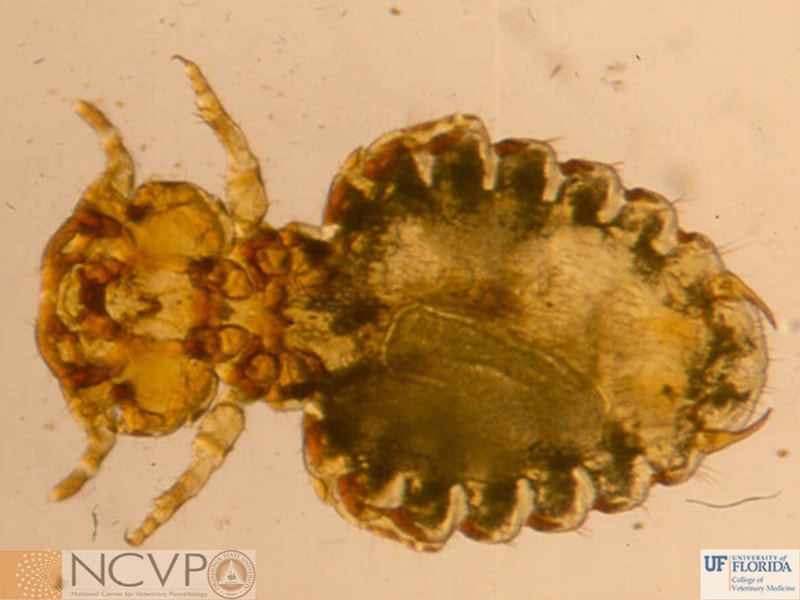
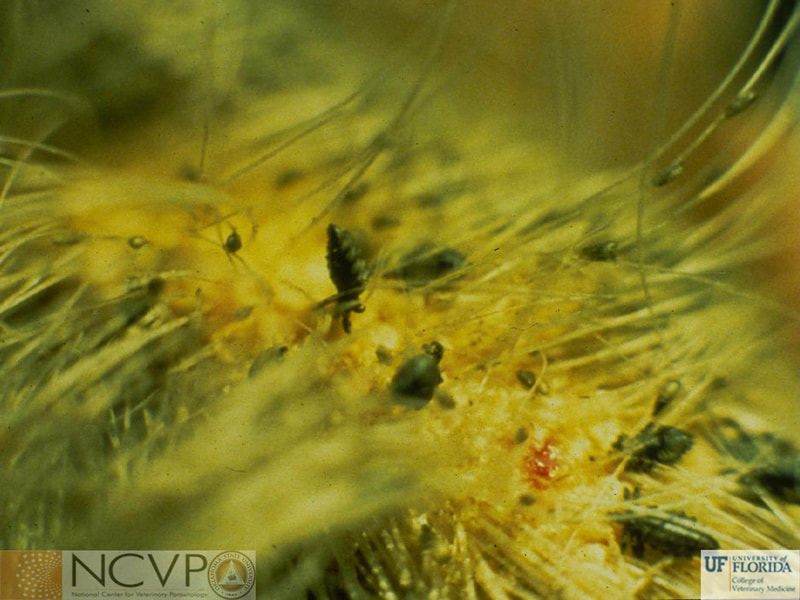
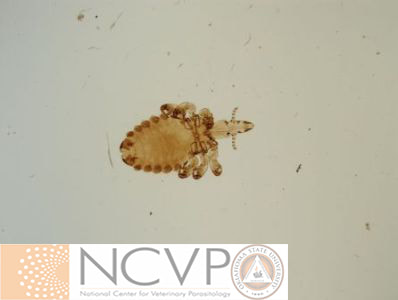
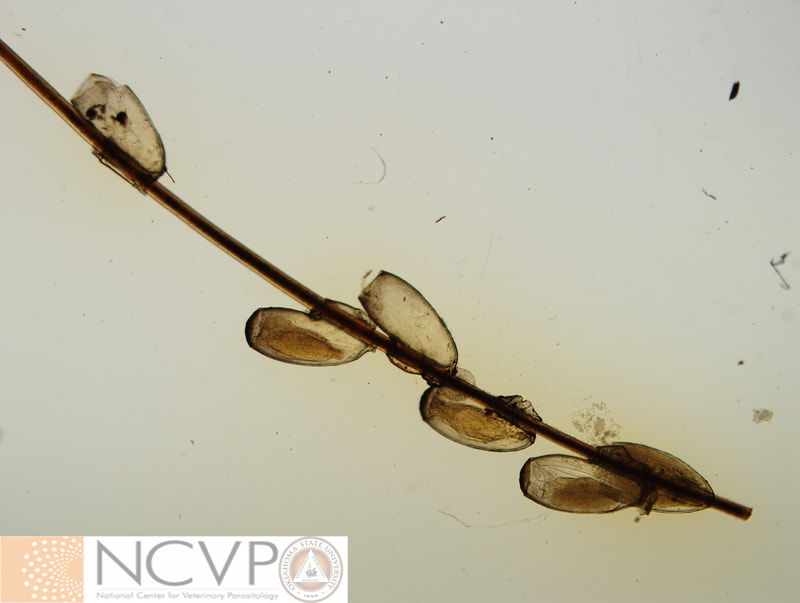
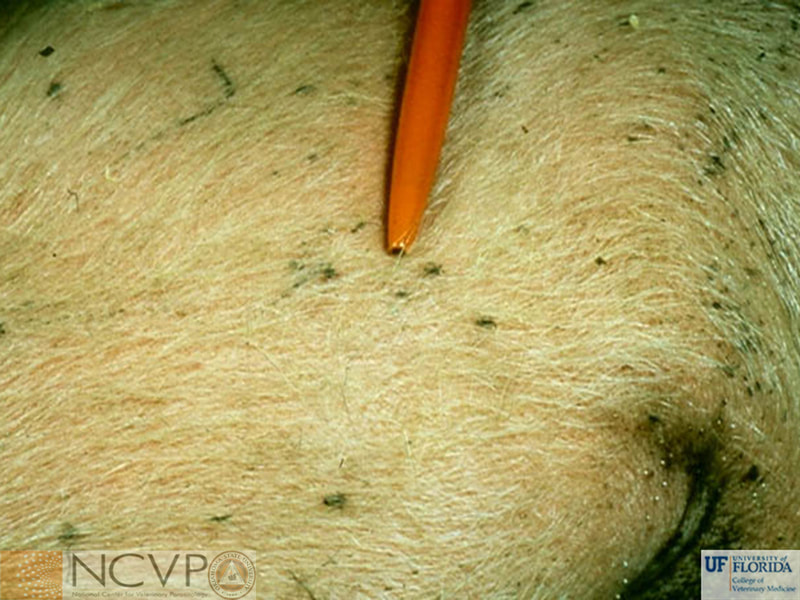
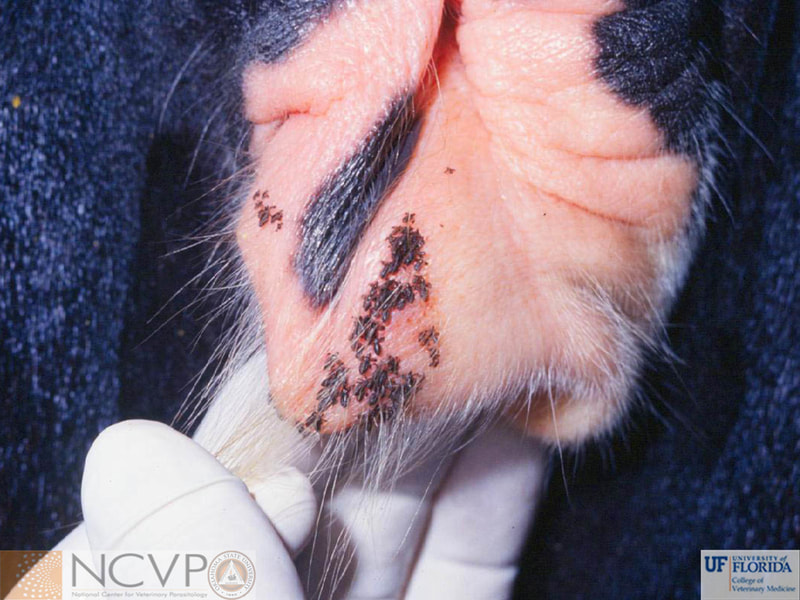
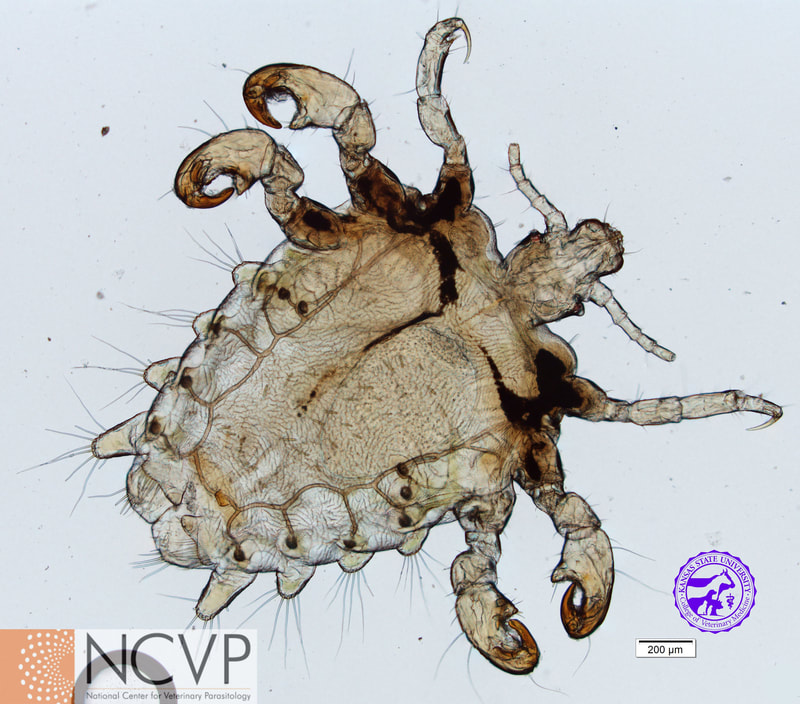
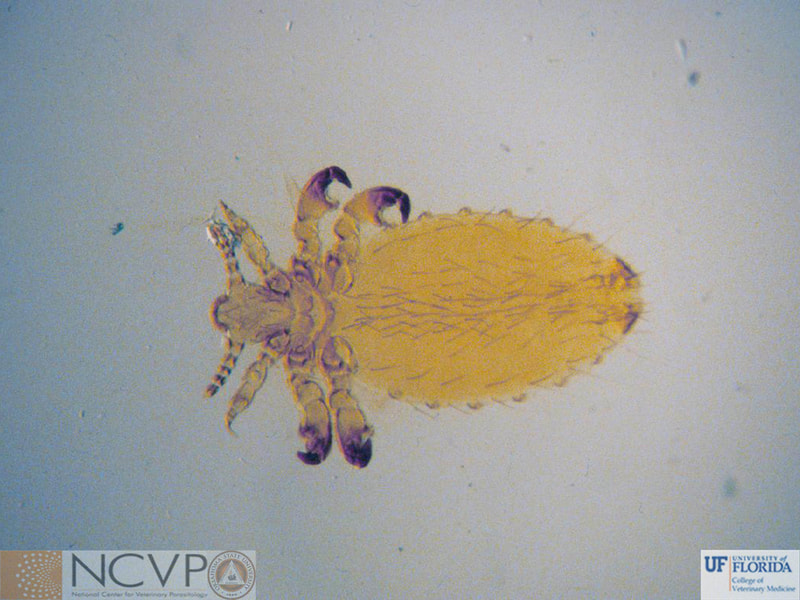
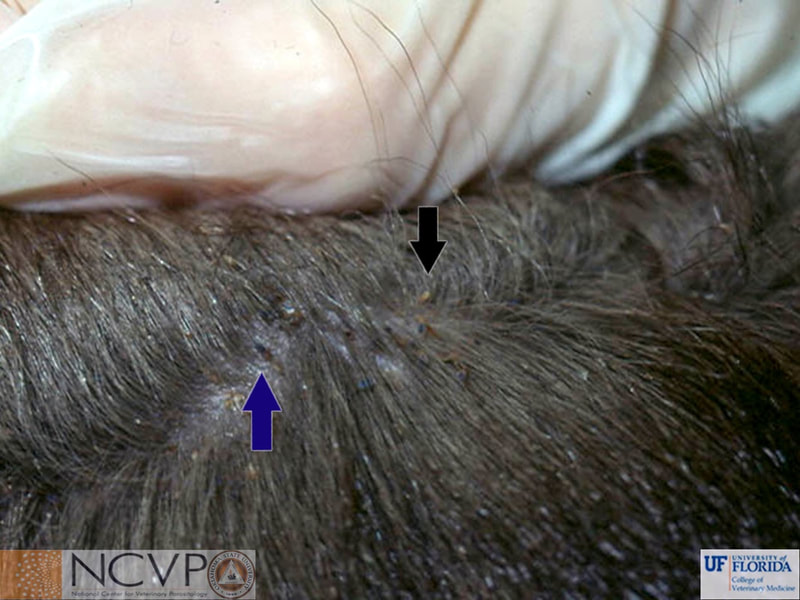
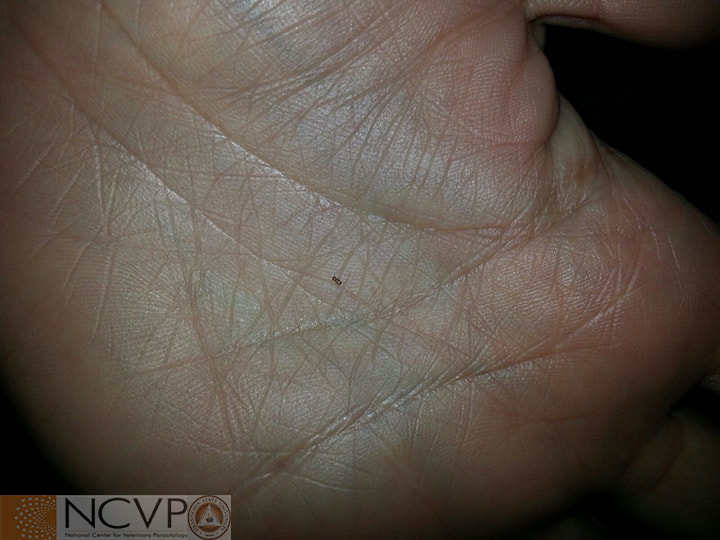
Anopluran - Sucking Lice Anopluran lice are found only on placental mammals. They feed on the blood of hosts via their piercing mouth parts, consisting of three stylets, and thus have been dubbed "sucking lice." Example genera include Haematopinus, Linognathus, Solenoptes, Polyplax, Pediculus, and Phthirus. Mallophagan - Chewing Lice Mallophagan or "chewing lice" are found on both birds and mammals, ingesting skin, keratin from feathers or hair, and secretions of their hosts. Three suborders are described - Ischnocera (e.g. Damalinia spp.), Amblycera (e.g. Gliricola spp.), and Rhynchophthirina (Haematomyzus spp.). |